Think your business is too small to be targeted? Think you’re not high profile enough to be lucrative for a cybercriminal?
Given 73 percent of small and mid-sized businesses in the U.S. experience cyber attacks annually, that definitely doesn’t seem to be the case.
– Brian Leger, Co-Founder of InfoTECH Solutions
SMB cybersecurity breaches can be incredibly expensive, costing millions of dollars on average. 60% of SMBs end up closing within six months after experiencing a data breach or cyber attack.
Moreover, small businesses face 350% more social engineering attacks than larger enterprises. Having strong cybersecurity measures in place is essential for small and medium-sized businesses.
If you’re uncertain about how to begin, this article will guide you through the steps necessary to safeguard your SMB. We’ll cover the most significant risks, prevention strategies, and how choosing the right cybersecurity partner can make a difference.
Some of the Most Common Cybersecurity Risks for SMBs
SMBs are up against many cybersecurity threats that can lead to severe outcomes. Here’s a rundown of the most frequent threats you should know.
1. Simple Passwords
Simple or predictable passwords are a major weakness. They can give attackers easy access to your important systems and information. Using the same password for different accounts or not changing default passwords can lead to stolen credentials and unauthorized entries.
2. Missing Multi-Factor Authentication
Relying only on passwords without multi-factor authentication (MFA) makes it easier for attackers to break into user accounts. MFA introduces an additional security step, like a code sent to a phone, making it harder for unauthorized users to access your systems and data.
3. Outdated Systems
Not updating software or installing patches makes your systems easy targets for attackers using known flaws. Cybercriminals often attack systems that aren’t up-to-date to steal data or spread malware, which underscores the need for regular updates and patching.
4. Insufficient Endpoint Protection
Devices connected to your network can get infected with malware or face other cyber threats. Using endpoint security solutions, such as antivirus programs and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, is crucial for stopping harmful activities on devices and safeguarding your network.
5. Incomplete Staff Training
A lack of cybersecurity knowledge among employees can result in accidental breaches, like clicking harmful links or falling for scams. Employees need proper training to avoid unknowingly putting your business at risk.
6. Threats from Within
Insider threats, whether deliberate or accidental, are a serious concern for SMBs. Employees or contractors with access to sensitive information or systems might misuse their access, leak data on purpose, or accidentally introduce cyber threats due to careless behavior.
7. Email Scams
Phishing attacks trick employees into giving away sensitive information or downloading harmful software through misleading emails or messages. These attacks can cause data breaches, financial losses, and harm to your reputation.
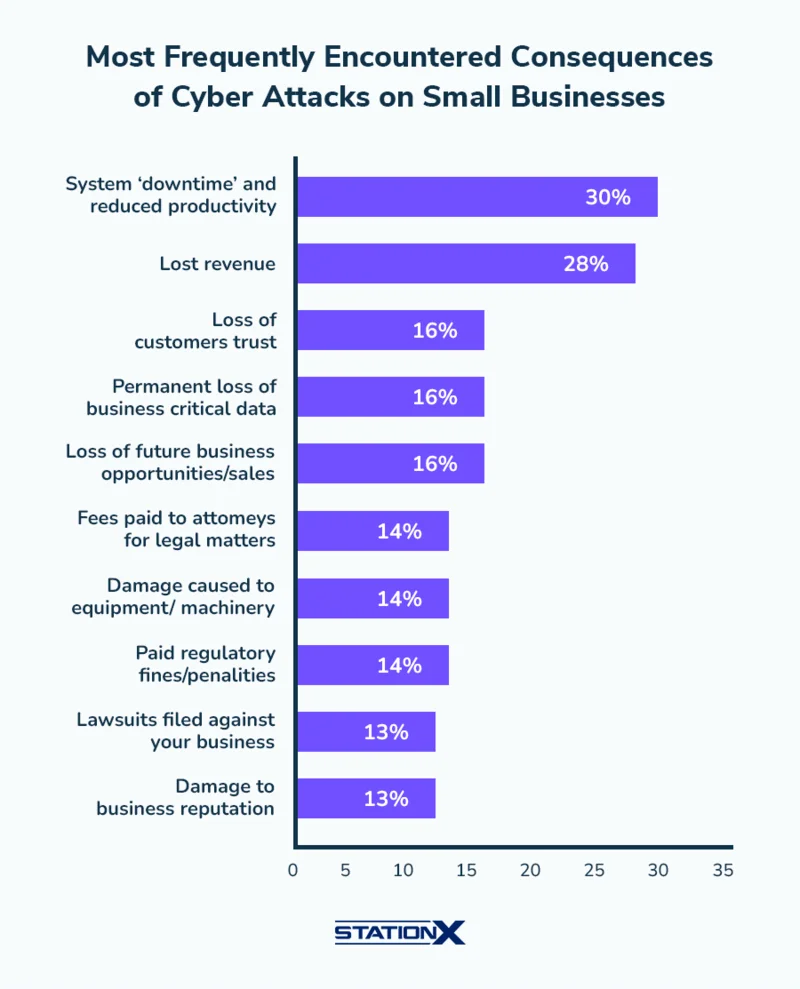
Source: StationX
10 Essentials for Boosting Your SMB’s Cybersecurity Posture
Your business must develop a clear cybersecurity strategy to shield operations, customers, and data from the increasing number of cybersecurity threats. Here are a few essential steps to do just that.
1. Educate Your Team on Security Basics
Set up fundamental security rules and policies for your team, like using strong passwords. Create clear guidelines for using the internet safely at work, including the consequences of not following cybersecurity policies. Also, define procedures for managing and safeguarding customer information and other critical data securely.
2. Safeguard Your Data, Computers and Network
Ensure you have the latest security programs, browsers, and operating systems to defend against viruses, malware, and other online dangers. Configure your antivirus to scan automatically after each update. Promptly install updates for other essential software as well.
3. Implement Firewall Security for Your Internet
A firewall consists of programs that block unauthorized access to your private network. Ensure your operating system’s firewall is active or install a free firewall from the internet. For employees working remotely, their home networks should also be protected by a firewall.
4. Set Up a Plan for Mobile Devices
Mobile devices pose unique security and management issues, particularly if they contain sensitive information or can connect to your business network. Require employees to use passwords on their devices, encrypt their data, and use security applications to protect against data theft on public networks. Also, establish a process for reporting lost or stolen devices.
| SMB Cybersecurity Checklist | |
| Essential Steps | Details |
| Educate Your Team on Security Basics | Set up fundamental security rules and policies. Educate employees on internet safety and managing customer information securely. |
| Safeguard Your Data, Computers, and Network | Use the latest security programs, browsers, and operating systems. Install updates and antivirus scans regularly. |
| Implement Firewall Security for Your Internet | Use firewall programs to block unauthorized access. Ensure remote workers’ networks are also protected. |
| Set Up a Plan for Mobile Devices | Implement security measures for mobile devices, including password use, data encryption, and theft protection. |
| Backup Your Important Business Data | Regularly backup critical data, including documents, financial records, and databases, preferably offsite or in the cloud. |
| Manage Physical Access and Create Individual Accounts | Limit physical access to computers and create unique user accounts for each employee. |
| Enhance Your Wi-Fi Network’s Security | Secure and hide your Wi-Fi network. Use strong passwords for your router to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Adopt Secure Payment Card Practices | Use secure tools and anti-fraud services for payment processing. Keep payment systems isolated from other applications. |
| Restrict Employee Access and Software Installation Privileges | Grant data access based on role necessity and restrict software installation to authorized personnel only. |
| Strengthen Password Policies and Authentication Methods | Require unique passwords and regular updates. Implement multi-factor authentication for additional security. |
5. Backup Your Important Business Data
Consistently create backups of critical data from all computers. Important data includes documents, spreadsheets, databases, financial records, human resources, and accounts receivable/payable information. Aim to backup data automatically, or at a minimum, do it weekly, and keep the backups offsite or in the cloud.
6. Manage Physical Access and Create Individual Accounts
Limit physical access to your company’s computers to prevent unauthorized use. Laptops, which can easily be stolen or lost, should be securely locked when not in use. Create a unique user account for each employee, requiring strong passwords for access. Administrative rights should be reserved for trusted IT personnel and key staff members only.
7. Enhance Your Wi-Fi Network’s Security
Ensure your workplace Wi-Fi is not only secure and encrypted but also hidden. Configure your router or wireless access point to not broadcast the network’s name, or Service Set Identifier (SSID), and secure your router with a strong password to prevent unauthorized access.
8. Adopt Secure Payment Card Practices
Coordinate with your bank or payment processors to use secure, verified tools and anti-fraud services. You may have extra security duties based on your agreements with these entities. Keep your payment systems separate from less secure applications and avoid using the same computers for payment processing and general internet browsing.
9. Restrict Employee Access and Software Installation Privileges
Avoid giving any single employee access to all your data systems. Grant employees access only to the data systems necessary for their roles and prevent them from installing software without approval. This approach minimizes risks and helps protect sensitive information.
10. Strengthen Password Policies and Authentication Methods
Mandate that employees use distinct passwords and update them every three months. To enhance security further, implement multi-factor authentication, which requires additional verification beyond just a password to access accounts. Also, check with your service providers, particularly those handling sensitive financial data, to ensure they support multi-factor authentication for an added layer of security.
Secure Your Data, Applications, and People With InfoTECH Solutions
Here’s the rule of thumb with cybersecurity: that which works today, may not be effective tomorrow. Cyber threats are always evolving, new vulnerabilities are always being found and exploited. Your approach to cybersecurity must, therefore, be proactive.
Proven Cybersecurity Services Near You
Routine assessments, regular updates, and ongoing staff training: are vitally important for maintaining a secure IT environment. It’s why SMBs turn to us. At InfoTECH Solutions, we bring over 20 years of expertise in securing businesses.
Whether you’re taking the first cybersecurity steps for your business or looking to improve your security posture, we can help you. Talk to us about how our proven cybersecurity technologies and processes keep businesses like yours secure.



