An information security policy is a set of guidelines that outline how a company manages and protects data. The goal of this policy is to encourage employees to follow the necessary practices to maintain data integrity and confidentiality.
“An information security policy establishes the groundwork for protecting your most valuable data and reducing the impact of potential cyber threats.” – Brian Leger, Co-Founder of InfoTECH Solutions.
A well-structured policy reduces your chance of a data breach. It also supports your compliance efforts and provides employees with the knowledge and resources they need to handle data properly. Clear communication of expectations helps prevent human error, which is the source of 95% of security incidents.
This article explores the essential elements of an information security policy. We’ll provide example policies, key elements you should include and how to create one for your SMB.
Key Components of an Effective Information Security Policy
Access Control
Access control specifies who can access, modify, or manage data based on their role. It restricts unauthorized access and ensures sensitive information is handled properly. Regularly reviewing permissions and limiting access to only what’s necessary helps strengthen security.
Data Classification
Data classification assigns sensitivity levels to different types of information. This helps ensure that sensitive data receives the protection it needs. By categorizing information, your team can apply the right data security measures to each type of data.
Maintain 24/7 Network Security for All Information Assets
Incident Response Plan
77% of organizations are without an incident response plan and you should not let yours be one of them. An incident response plan outlines how to handle security incidents quickly. It includes steps for minimizing damage and disaster recovery.
Compliance & Auditing
Set a schedule for regular checks to ensure your security standards meet compliance requirements. Audits help identify gaps and areas for improvement. This process ensures that your security policies remain effective and up-to-date.
Information Security Policy Examples
Acceptable Use Policy (AUP)
An acceptable use policy defines the proper use of company-provided devices, networks, and software. It informs employees about permitted activities and those that are restricted. The policy helps protect the organization from legal and security risks by outlining clear guidelines.
Social Media Policy
According to CloudSecureTech, 25% of employees click most of the links they see on social media. That’s why you need a social media policy. Don’t assume social media safety is “common knowledge.” Set a policy to govern how employees use social media platforms. Remind them not to share confidential data and address the risks posed by phishing and social engineering attacks.
Internet Usage Policy
An internet usage policy sets clear rules for browsing and using the web on company networks. It restricts access to certain websites known for security risks and prevents the use of unauthorized software or file downloads.
Many companies use web filtering tools to minimize possible exposure to online threats. Here is how that works.
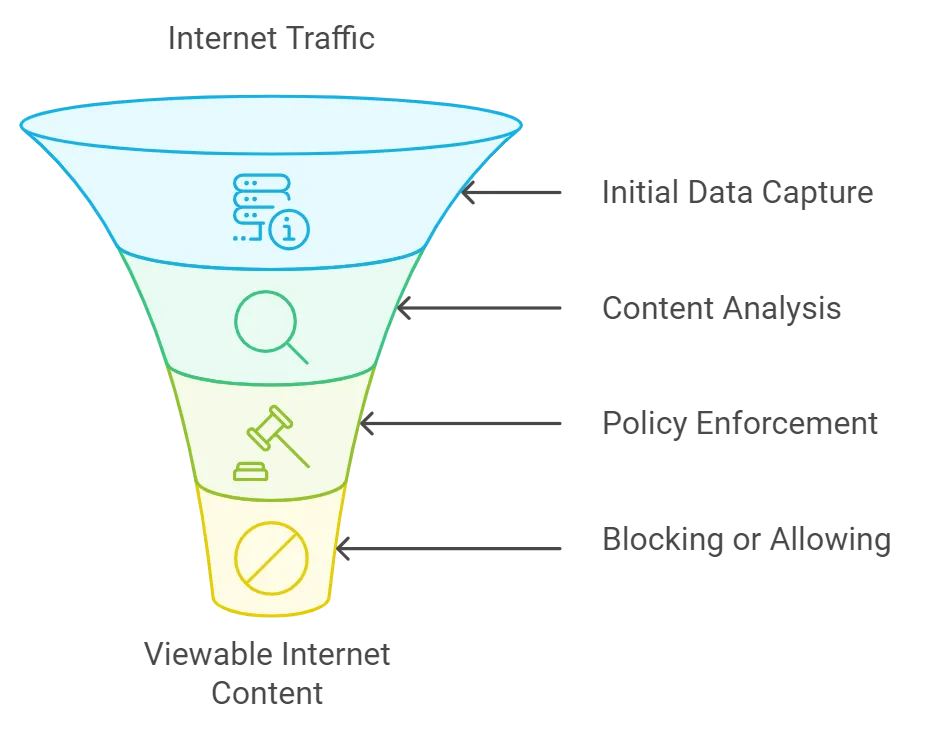
Removable Media Policy
A removable media policy limits or restricts the use of USB drives, external hard drives, and similar devices. You may ban the use of unapproved devices to reduce the chance of introducing malware into the network. Remember to also outline secure ways to transfer data for cases when the use of removable media may be necessary.
End-of-Life (EOL) Systems Policy
An EOL policy ensures that outdated systems and software are retired in a secure manner. This includes migrating data to supported platforms, deleting old data, and upgrading to the latest versions to avoid security vulnerabilities. The policy also prevents the continued use of unsupported software.
Remote Work Security Policy
This policy sets rules for secure access to company data and systems when working remotely. You may enforce the use of virtual private networks (VPNs) or the use of encryption and secure authentication methods for remote access.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) Enforcement Policy
This policy requires the use of MFA to access critical systems and sensitive data. It specifies when MFA is required, who must use it, and which technologies are allowed, such as mobile apps or hardware tokens. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
How to Create a Sample Information Security Policy: Step-by-Step
1. Risk Assessment
Begin by identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities within your systems. This step helps to map out the specific risks your business faces and sets the foundation for designing appropriate security controls.
2. Define Objectives
Once risks are assessed, define your security objectives. These objectives should outline the purpose of the policy, align with business goals, and serve as a guide for implementing the right security measures.
If you need a hand with brainstorming, here are a few example security objectives.
| Enhance Incident Response Agility | Streamline processes to improve the speed and effectiveness of response to security incidents. |
| Integrate Security with DevOps | Embed security controls early in the development lifecycle to prevent vulnerabilities in applications. |
| Strengthen Vendor Security | Ensure third-party vendors adhere to the company’s security standards to minimize external risks. |
| Reduce Attack Surface | Continuously identify and minimize exposed systems, services, or data that could be targeted by threats. |
| Automate Threat Detection | Implement advanced automation to identify and respond to threats in real-time, reducing manual intervention. |
3. Develop Procedures
Create specific, actionable procedures that address the identified risks. These procedures should be clear enough for employees to follow to ensure that the policy is functional. Testing your procedures in a controlled environment is a good practice to verify functionality.
4. Employee Training
Implement regular training programs for employees to keep them aware of their role in maintaining security. Training ensures that all staff understand the procedures and stay vigilant against evolving threats.
| Talk to Expert Cybersecurity Consultants in Louisiana | ||
| New Orleans | Lafayette | Baton Rouge |
Flesh Out an Information Security Policy Template for Your Small Business With Our Help
The right information security policy will protect your brand reputation, data integrity, and business continuity. What you read were all general guidelines that can help you get started. However, we recommend that you dig deeper to craft a more detailed policy for your unique needs.
InfoTECH Solutions employs cybersecurity consultants who can help you with that process. We’ll get to know your business needs in detail and compare them to industry standards. From there, we’ll work with you to create a policy that balances both.
Reach out today to get started.



